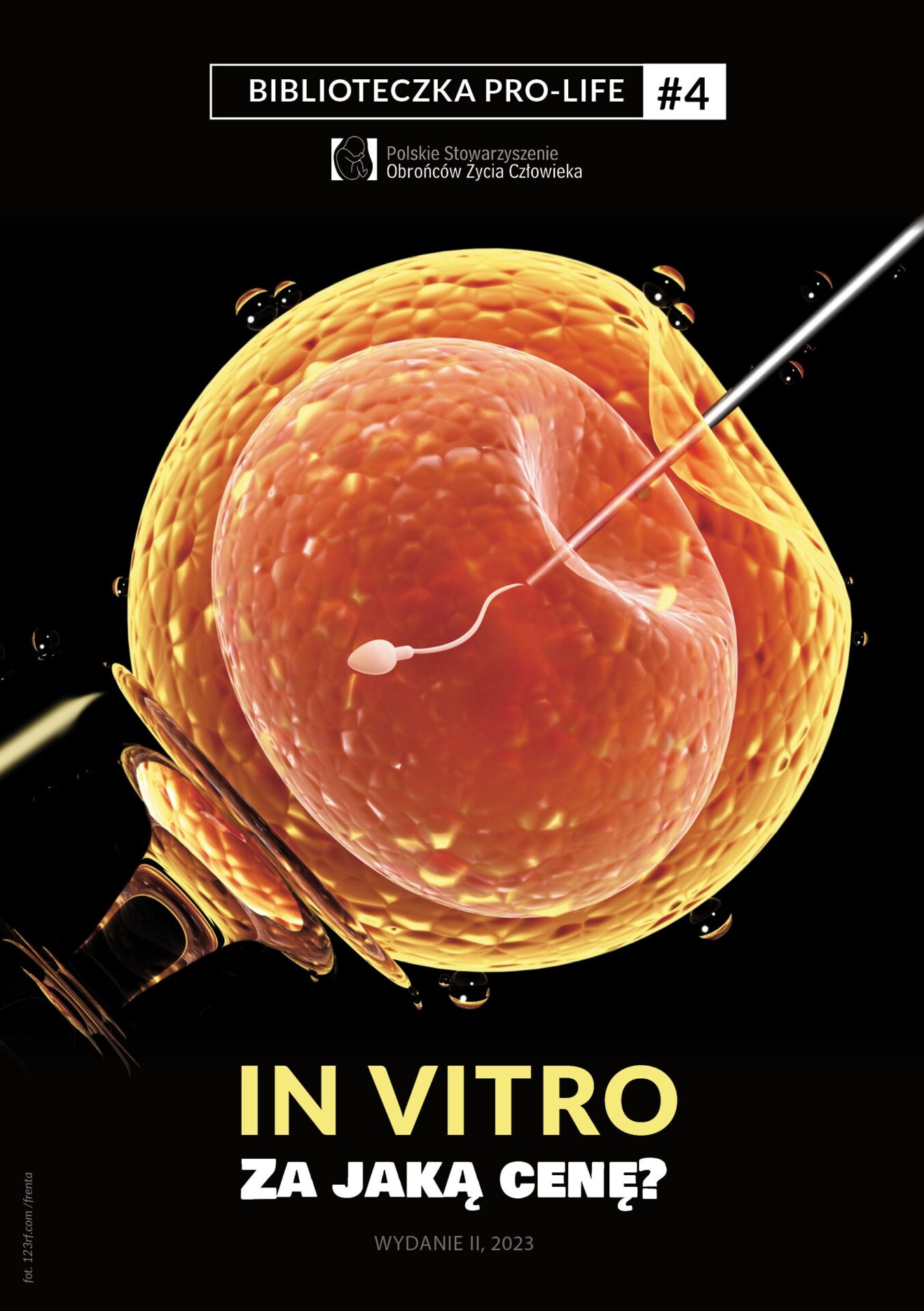
A vote on in vitro financing from public money was scheduled in the Sejm on 28 November. Why are we against it? To answer that question, you request to know the stages of the procedure. And then remember that the embryo is human, due to the fact that if not, what is it?
In vitro steps
- Hormonal stimulation – the first phase of the in vitro procedure is controlled hormonal therapy, which leads to ovarian hyperstimulation. The female takes very advanced doses of hormones to origin simultaneous growth and improvement of many eggs. Usually, during specified stimulation, it matures from 5 to 20 oocytes, while in the natural menstrual cycle, maturity usually reaches only 1 egg cell. (According to the current Polish law, 6 embryos can be created. Exceptions: age of female 35+ or 2 unsuccessful in vitro procedures).
- Ovarian punctuation – a procedure for the collection of mature eggs. A puncture is performed through vaginal vaulting and the ovary is removed from the ovary. The puncture lasts 10 to 20 minutes and is performed under local or short-term general anaesthesia. At the same time, erstwhile the puncture is performed, the man, masturbating, gives the sperm to the sampler in the room. If the semen cannot be obtained in this way, it is possible to collect the semen surgically, as well as to usage previously frozen semen for fertilisation.
- Evaluation of reproductive cells. Choice of full mature eggs.
- Insemination – collected reproductive cells are placed on laboratory scales in the incubator. Within 24 hours, several, several, many, and sometimes even more than twenty, embryonic children, emerge.
- Breeding and selection of embryos – after successful fertilization, all human embryos formed are stripped of the layers of grain cells and observed for the next 24 hours. The best, according to the doctor, will be transferred to the uterus. Others will undergo cryoconservation (freezing in liquid nitrogen at a temperature of minus 196 degrees C) to inhibit their development.
- Embryo transfer – one, 2 or more children are transferred to the uterus utilizing a catheter. After the transfer, the female continues to take pharmacological measures to increase the chances of embryo implantation.
- Pregnancy test – a pregnancy test is performed after about 2 weeks. If positive, correct implantation of the embryo or embryos is confirmed by ultrasound examination. If the in vitro procedure fails, it may be repeated.
In view of the in vitro pushy advertising of the “right to child” for all average person, it is hard to realize what is the wickedness of in vitro fertilization. The shortest answer could be that the dignity of man, including the unborn, cannot be devoted to the desire to have a child. Although in vitro children are created outside their mother's body, from the first moments of their lives on the Petri dish they have the inalienable and inviolable dignity of a human person. Their life has already begun and is as full as the life of children born naturally! They enjoy all human rights, especially the most crucial of them – the right to life and development. Unfortunately, it is violated at many stages of the in vitro procedure, which is inextricably linked to embryo segregation and the death of many of them.
Only 7.5% of human embryos resulting from the usage of artificial insemination methods are born alive (American Society for Reproduction Medicine). In vitro is not indifferent to the wellness of the parent and child.
Among another things, the hazard of ectopic pregnancy, duplicate and multiple pregnancy, abortion increases. another complications: ovarian torsion, possible complications after punctuation after oocyte collection, complications after transfer, premature delivery, inhibition of intrauterine growth. Women get depressed more often. A advanced proportion of pregnancy after in vitro ends with an imperial cut.
Within 15 years of in vitro exposure, women have an increased incidence of tumours following hormonal stimulation. The hazard of ovarian cancer is nearly quadrupled, and the hazard of breast and molar cancer is importantly increased.
The in vitro procedure increases the hazard of chromosomal disorders, including Turner syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Down syndrome and another genetic diseases.
At least 9 percent of children conceived in vitro are born with severe heart defects, oesophageal growth, anal growth, lip divided and palate, defects in the improvement of the genitourinary strategy in boys. In children conceived in vitro, up to 5 years of age, almost twice as many surgical procedures as in children conceived naturally.
In vitro increases the hazard of premature, perinatal death, dead birth, low birth mass, foetal giantism and cerebral kid palsy. Children are at increased hazard of developing fetal neurosis, leukaemia and retinal disease. In addition, the hazard of tumours increases sevenfold in the group of children who were born with another serious congenital defect.