To say that generals are preparing for wars that have already taken place has become very fashionable again. Especially in Poland, where we fear that the future armed conflict in Europe may besides affect our country. Concerns about the possible of the Polish Armed Forces, as well as whether the direction of their improvement is right, have become the subject of common, social considerations.
In this context, many discussions are being held to answer the question: what will the future battlefield look like? The answer to this question is never simple, and it is only war that verifies erstwhile assumptions. On the basis of historical experience, however, it is possible to find the conditions in which the most accurate models of the future battlefield were created, and even to identify people who revolutionized the way wars were fought. Of course, searching for rules and simplifications can distort the image of reality, but it is worth doing specified intellectual exercises in order to find the optimal conditions in which an appropriate model of future conflict management (on a strategical scale) and conducting a fight (on an operational-tactical scale) could arise.
There is no uncertainty that, in principle, in modern and modern states which were conceptually and technologically best prepared for war were usually part of the Western cultural circle. In which innovation and cultural-technology-industrial revolutions occurred earlier than elsewhere. Hitler would never build his armored divisions if he had no access to modern German manufacture and did not invest in infrastructure. Napoleon would not have created his armies had it not been for the French Revolution and the decree of 23 August 1793 on mass mobilization, which in effect gave him access to a immense number of decently motivated (beating for France or revolution alternatively than in the king's interest) recruits.
However, the evolution of the battlefield occurs faster in the given place and time not only due to the appropriate socio-economic and technological conditions. besides due to the request for a minute (a emerging threat) or intention (a war/conquest planning). At the same time, it should be remembered that the best teacher is practice and the top advancement in uncovering the best way to fight was based on war experiences.
This is why it is said that during peacetime generals prepare for wars that have already been. This is due to the fact that the military does not receive any fresh data from war experiences. They can only analyse past conflicts and supplement requests for fresh solutions not yet tested on the battlefield. Which does not always lead to a appropriate imagination of the future war. Besides, it is impossible to do specified a projection due to the fact that 1 should inactive have the ability to see clearly and correctly foretell erstwhile precisely this "future war" will take place? How long would it last? It is simply a fundamental difference whether we are preparing for a war that will blow up, for example, in 2025 and will last 3 months, or until the conflict of 2050, which will last a decade.In both cases, priorities should be allocated differently. In the first, it would be essential to rapidly implement the existing solutions as far as possible. In the second, it would be better to wait for the improvement of fresh technologies and to make existing technologies, e.g. only about 2040, to start implementing completely fresh solutions. In manufacture and in the army. And not to waste resources building and maintaining production lines and armies from 2020 to 2030, which would consume resources that could be allocated to investigation and innovation.
Therefore, not only are the conditions under which the concept of the future battlefield is created, but besides the assumptions for: parties, places, time and dimension of the future war..
And that's where the biggest problem comes in. How do you specify these variables? Historically, time and place of conflict were determined by aggressors. Which gave them the chance to decently plan and prepare the state and army for a future armed conflict. Countries that are preparing to defend themselves are in a much worse position here. due to the fact that if they start arms besides soon, their army will most likely prove obsolete on the battlefield. erstwhile the preparations for the war are late, the military may not be ready to launch with the enemy.
Therefore, in the case of a state with a strategy and defensive doctrine, the most crucial thing is that:
- The future opponent and the reasons why he would be able to accomplish his goals through war.
- Suitable for him the minute to strike, besides in terms of the determination of readiness to take aggressive action (time).
- A convenient place to attack.
Without specified assumptions, it is impossible to foretell what a peculiar conflict will look like, even from the conceptual and method side.
However, this article is not to answer questions: whether, when, where and with whom Poland will wage war in the future. The aim of the survey is to effort to supply a general indication of trends and regularity that will accompany future wars. This involves full-scale wars, not military skirmishes, hybrid actions, or military operations. specified limited actions should not be excluded – on the contrary, they should be taken into account as highly likely – but their objectives, and so the way in which they are carried out and how they are carried out, vary widely. Therefore, in specified cases, it is always essential to nuance what conflict and erstwhile it is meant to be able to outline possible scenarios and risks associated with it.
The subject of the following considerations is to identify possible ways of conducting conflicts in future full-scale wars, with the aim of killing the state-sacrifice. For these or another reasons. In another words, in order to succeed, it would be essential to defeat the full country and force surrender or unconditional surrender to the full extent.
Domains and conflict phases
It is worth setting out at the beginning the levels on which war may be fought, as well as the different phases of clash between countries. This is best done by describing the order of action of the attacking party. For in the first period of conflict, she usually has the initiative and decides erstwhile and in what field the clash takes place.
Pre-war phase
- Political attack aiming to weaken or even isolate the opponent internationally (to discourage 3rd parties from helping the future victim), as well as to gain allies and ground-floors. The optimal option is to accomplish the strategical goal without the request for military force – this kind of aggression can last even for years.
- Economic and economical Attack aimed at weakening the victim state or its allies and exerting political force on them (vide reduction in Russian gas supply to the EU in 2021) years/months before the war
- Information attack In order to make confusion in enemy decision-making centres of the army and society, it is both intelligence-agency activities as well as those legal in the information sphere of the opponent, but besides in its possible allies – which usually takes place months/week before the armed invasion (an crucial symptom, as it already shows that the aggressor is considering the military option).
- Hybrid attack, i.e. real actions aimed at weakening the vigilance of the opponent and his allies, focusing their attention and resources on the site chosen by the future aggressor (vide ‘migration crisis’ on the Polish-Belarusian border) – which usually takes place weeks/days before the attack
- Cyber attack in order to subdue hostile defence systems and state resilience, days/hours before the attack.
- Attack of peculiar forces or V column In order to gain the starting advantage for operational troops, hours/minutes before the attack.
Armed conflict phase:
- Space attack to neutralise enemy satellites, increase the advantage in the space domain or deprive the enemy of that advantage.
- Air rocket attack utilizing air, land and sea forces.
- Military attackland.
With specified a timetable, it becomes clear that the state must be prepared to wage war on each of these planes. From political to hot phases of armed conflict.
PREVIOUS STAGES
Political and economical Security

Undoubtedly, the domain of political conflict requires adequate skills and awareness on the side of the country's decision-making elites. A key political component is the acquisition of the best global alliances and guarantees, as well as an adequate visibility and exploitation of the convergence of interests with 3rd countries. Political isolation of the opponent should besides be sought, while neutralising its communicative and arguments utilized for persuasion. To this end, the State should have an extended analytical apparatus that will supply the intellectual background of politicians.
However, preparing the state for economical and economical combat requires much more effort and investment. The aim is to accomplish as much economical and financial autonomy as possible and to diversify sources of strategical resources. Thus, the more you spend on investments that increase its resilience on the discussed levels, the stronger it will be politically and at the same time more resistant to external pressure. At the same time, this must besides affect investments in the arms industry, which, on the 1 hand, should have access to natural materials and, on the another hand, have adequate capacity to keep the armed forces in the war.
Financial institutions must play an highly crucial function in all of this, and they will receive the essential tools from legislators to manage the financial capacity of the state in times of crisis or war. This includes legislation.
Importantly, In preparing wars, the state should invest in structures of links that will give it the chance to exert force on its opponent, or (more importantly) on 3rd countries. Building economical and economical dependence is an effective tool for maintaining the loyalty of existing allies and acquiring fresh ones.
Information anti-access bubble

While in the course of the political war the 1 with better channels of communication and closer contact with another actors on the global phase has an advantage, in the course of the information war, the side that will better control the flow of information in its infosphere, and will besides be able to usage another channels of communication to scope the elites and societies of its opponents and its allies. In the digital world, erstwhile information appears and reaches audiences in real time, it is highly hard to filter or fight enemy narrative.
Under specified conditions, the anticipation of cutting off our own society from hostile transmission may be crucial. This is precisely how their information war against the West is presently waged by regimes from Iran, Russia or even China. While in peacetime this can origin more harm than benefits (especially long-term) in and before the war, cutting off hostile information communications can be an effective method of defence against an information attack.
Several methods can be utilized to deal with this problem:
- Neutralizing the opponent's narrative through its own information-propagand activities, so that its communicative is completely ineffective for us and allies. This can be done e.g. by embarrassing the opponent or pre-stigmatizing the communicative that he could usage (well done by Ukrainians now). The point is that society but besides the elite of the country under attack should not trust messages that favour the enemy.
- Isolation of the enemyinfosphery from the global information network (e.g. no emissions of enemy tv and radio channels, blocking enemy news portals on the Internet), although this kind of solution does not supply any guarantees, especially erstwhile the opponent uses our own infosphere to spread his communicative (e.g. through influence agents etc.).
- Isolating your own infosphere from the global information network and its overall control (vide Russia, Iran China), especially erstwhile the opponent uses our infosphere not only to advance his own communicative but besides to communicate with her supporters or influence agents (considering as a station or communication centre from where they flow – in a more or little hidden way – guidelines).
The first solution seems to be the most effective if we measure based on the experience of the ongoing Russian-Ukrainian war. However, it should be remembered that not in all war will the opponent have specified a scorned reputation and at the same time will be as clumsy in the information-propagand domain as the Russians are now. At the same time, 1 good disinformation action is adequate to confuse the opponent, weaken him and change the destiny of the war.
Moreover, the isolation of hostile infospheres may in many cases be impossible, especially erstwhile this depends on the decisions of individual countries on the global stage.
As a consequence, even a democratic state administration should be able to technically isolate its own infosphere. So to prevent it from transmitting from the outside. Both tv and radio and the Internet. With Such a method can only be utilized in democratic conditions under exceptional conditions (i.e. like a close threat of war or an already ongoing conflict). due to the fact that society must be full convinced that specified a drastic measurement limiting freedom of expression is absolutely necessary. Otherwise, the state's usage of censorship and information blockades will be read as an component of repression, which not only will not halt hostile narrative, but will even make it easier for it to penetrate our infosphere and public awareness (mechanism: information blocked by authorities is surely true).
Information troops
There is besides no uncertainty that a fresh kind of armed force of the future battlefield will become troopsInformation. Even if they're not officially formed. We have entered a fresh era of propaganda war, which presently has a digital dimension. So its scope is much wider, global. In preparation for the future war, the state should invest in its own media, which will operate in the hostile infosphere or will be able to scope it. However, the most crucial field of information-propagand combat can be the infosphere of our but besides enemy allies. The conduct of an open war between states importantly increases the resilience of the societies active in the conflict to a message conducive to the enemy. However, specified resilience may be lacking in 3rd countries whose commitment (or deficiency of it) may decide the destiny of war.
E.g. For Ukrainians and Russians, the Western infosphere is simply a precedence area for propaganda and information activities. It is mainly in our media space that there is simply a war on this plane. The precedence nonsubjective of informing or disinformation is: Americans, British, French, Germans and Poles, not Ukrainians or Russians.
Consequently, the biggest investments to build the right: possible and information resources, must be made towards our possible allies and possible allies of our future enemy. besides for this reason, that a message that is incapable to penetrate straight into the enemy infosphere can go there and origin havoc through the infosphere of an enemy ally. For example, the russian propaganda has small chance of generating an effective reaction in Polish society, but what if precisely the same communicative begins to be preached by an American journalist, scientist or politician? And will it be shown in Polish media or spread on the Internet?
Services, services and services

What have we learned from the experience of the migration crisis on the Polish-Belarusian border? The first and overriding conclusion should be that the regular army cannot be utilized to respond to hybrid threats. It cannot be that 1/3 of the soldiers are active in guarding the border against refugees. frequently hundreds of miles from its bases and weapons and equipment warehouses. It must be clearly written, this part of the army was then incapable to execute its basic tasks.
A modern state that intends to prepare for the threat of war in the coming years should invest in the expansion of police forces(including anti-terrorism),Border Guards, civilian and military peculiar units, as well as military formations, i.e. Territorial Defense.
The Army has 2 basic tasks: deterrence and combat against the enemy. The military should be utilized to deal with hybrid activities only erstwhile they are conducted utilizing an enemy army. Engaging soldiers, who frequently service roads and complicated equipment, to tasks not requiring the usage of this equipment is simply a waste of resources and weakens the state's defence.
In order to prevent this negative phenomenon, the state must have a well-developed safety apparatus, which will take on the burden of dealing with various types of crises. Caused intentionally or not (i.e. like floods and another natural disasters). At the same time, services – during the war – could take over the task of securing the backdoor by diversionary actions or even organisational chaos (e.g. traffic jams on the roads etc.). Support army logistics as well as managing resources among civilians.
Crisis management
The crisis management centre is evidently something that functions in all country (in 1 form or another). And it surely should be prepared for all kinds of scenarios. However, 1 cannot think only about responding to events.
A country that prepares for a future war should have services specialised in special, diversion and hybrid activities. Have ready-to-use scenarios and procedures, as well as the essential resources (including personal) to implement scenarios that will trigger crises in 3rd countries if necessary. The enemy, but besides his and his own allies. You should have prepared scenarios for different circumstances. possibly only a circumstantial incidental would be inclined to discourage our enemy's allies to engage in conflict? possibly a circumstantial incidental could convince our allies to act and aid us?
Such actions require extraordinary care and caution in preparation. They cannot be left to destiny or action ad hoc. Preparations for the above-mentioned peculiar operations sometimes last years, which must be carried out by people absorbed only by these tasks. In separate services or cells, which are accessible to a fewer people in the country.
Mercenaries and “green men”
In fresh days, in Poland, a heated debate on the dangers arising for our country from Wagner Group mercenaries, due to its future deployment in Belarus. The question should be asked, why are we so worried about the war on the part of Prigozhina and his people? This is due to the fact that Poland does not have its own equivalent of Wagner Group or Blackwater. True, these notorious organizations could origin problems even for their own customers. Nevertheless, neither Russia nor the US have given up this form of hiring professionals since the war. There's a good reason for that. any tasks can be performed by private entities with as good and sometimes better effect than the army. There are even situations where private companies can solve problems in ways that state services would not be able to act. In the case of a state with a defensive strategy, the hired groups may be a tool for a symmetrical response. And more than that.
If the enemy professionals from a private company started to operate in our country, then, on the 1 hand, engaging an army would weaken its defence potential. On the another hand, civilian services or volunteers from the WOT might not be able to manage the task of stopping the opponent, which would exposure the state and its services to image embarrassment. But if Wagner's Group were to send Chopin's syndrome... specified an instrument would increase the chances of winning the opponent in a performance way.
Let us besides imagine a script in which the masses of immigrants nodding on the Belarusian side of the border abruptly – due to frustration – begin to origin problems. Not Poland, in which they are not admitted, but Belarus.
Another usage of private (although not necessarily detached from state control) military organisations could be sending them to aid their partners in crisis situations. A situation where, for example, the protection of president Zelenski would be performed by a Polish company would surely affect our relations with Kiev, but besides our image internationally. At the same time, it would not make the hazard of clash between Polish soldiers and Russians.
This kind of script should be ready, not to be implemented immediately, but a well-prepared state for war should make specified options.
Protection of critical infrastructure
Surely 1 of the overriding tasks for a country preparing for aggression is to guarantee the safety of its own critical infrastructure. As well as taking care of the alternative, if for any reason the opponent could halt the operation of this infrastructure.
Cyber-war

Today the request for cyberspace troops is clear. However, the precedence of specified formation should be to have the possible to carry out offensive activities. Impacting the enemy's space. Of course, securing your own cyber sphere is equally important, while in an IT conflict you cannot defeat your opponent by acting only in the defense. The defensive stance can only at best impede or hold the actions of the enemy, which are supported in digital space. The object of planning a possible cyber attack should be not only cybernetic military infrastructure but besides civilian.
The key is besides the ability to usage civilian human and intellectual resources to fight on a cybernetic level. To this end, cyber troops should be liable for building appropriate infrastructure (ICT system). This should service during the war to integrate civilian resources into cyber-armies possible and let for coordinated action. Cyber-militarythey must be prepared to exploit the enthusiasm of civilians and their willingness to defend the country in the cyber sphere. Civil IT specialists specialising in network safety issues can practically become full-value cyber soldiers overnight.
Moreover, specified a human resource management strategy should be developed on all militaryly applicable levels. Before the war, the state should make a database of individual data for citizens who have unique and needed army capabilities. So, for example, after mobilization, a individual with experience in handling drones or trucks did not end up a light infantry shooter.
CONFLICT FACT
In this section of the study, I will effort to systematically identify the changes we are seeing present and what trends are expected in the future. In matters of finance and investment, it is frequently said that if an uncle – who is not a specialist in the field – at a household gathering says that something is profitable and should be bought, then it is advanced time to dispose of assets of this kind. The popularization of military themes – caused by the outbreak of war – made the above example besides fit. If an uncle talks about the future war during a household meeting, it is likely that thousands of scientists, specialists and military scientists around the planet are working to make the conflict look completely different.
Star Wars vol. 2?

The designation of future or current battlefields led from outer space has become crucial for modern armies. Space capabilities besides let you to keep communication or transfer data (video starlink). The advantages of this domain are already impressive, and the possible of space technologies and their applications on the battlefield will grow. There's no question about that.
Since this fact is unquestionable, this means that the overarching nonsubjective of present or future work on military capabilities in the domain of space will be to find a way to neutralise the enemy's superiority in space or to defend his own cosmic advantage.
On the 1 hand, this leads to the conclusion that there will be a fast improvement of offensive weapons capable of damaging targets in space and, on the other, space defence systems will be created. However, this is not the most crucial conclusion for an army preparing for a future war. Before we get to that, let's sum up:
Current improvement direction: space designation and data transfer systems (including communications)
Future battlefield (expected abilities): The precedence will be to gain an advantage in space and keep it (development of space defence systems) and in the case of a weaker country, The goal is to neutralize the enemy advantage in space. (development of offensive systems, gross targets in the space domain).
Necessary possible for the future army: The ability to cope and operate effectively without space systems, which allow, among others, recognition, location (GPS), connectivity, data transfer.
Thus, in the future war, armies may turn out to have lost the capabilities provided by systems located in space as a consequence of certain actions. Thus, An highly crucial competence may be the ability to fight without the support of this domain.
Broken decision loop

Similarly, communication, communication and combat management procedures should be considered. present we are looking at the direction of technology improvement and the way in which war is waged towards full networkocentricity, which has a immense impact on the efficiency of joint action.
At the same time, the precedence for future commanders will be to break the decision loop of the opponent and neutralize his strategy of governing his subordinate troops. So with the improvement of systems like IBCS, expect the improvement of offensive systems that will be able to jam the communication of the opponent and interrupt the transfer of data between its units.
Current improvement direction: networkocentricity
Future battlefield (expected abilities): the usage of advantages resulting from the digitisation of the battlefield and, on the another hand, the improvement of offensive systems enabling information and communication isolation of the opponent's units
Necessary possible for the future army: maintaining analogue communication skills and conducting activities independently of the information systems used
Written by: Buying the latest book: “#This is our war”, in which you will find analyses concerning, among others, the interests of Poland in the context of the war struggles in Ukraine; the large strategy of Poland in the context of the construction of the armed forces of Poland; relations between Poland and Ukraine present and in the future. In the package with "Third Decade" cheaper! All books ordered by the blog by the end of July 31 23′ will be signed
Package: #This is our war + 3rd Decada
Debotisation of the battlefield?

The modern level of technological development, as well as experience from Ukrainian battlefield clearly indicate that unmanned devices are becoming increasingly important. Thus, by analogy to the way above, the following points can be drawn:
Current direction of the ditch: robotisation of combat fields and strategy autonomy,
Future battlefield (expected abilities): Unmanned neutralisation systems, including autonomous weapon systems (anti-drone systems)
Necessary possible for the future army: the request to keep the ability to execute the task by soldiers
Such conclusions – in view of the universal communicative – may prove to be rather primitive. Since advancement is taking place, it should be assumed that it will enable war to take place in a completely different way than before. However, this is just as general as incorrect in this case.
With the advent of artillery and aviation, the battlefield became more complicated in management, but this did not affect the usefulness of another formations. The power of artillery did not lead to the withdrawal of infantry, and the aviation did not destruct the armored cavalry. All these formations turn out to be needed to this day, and it will most likely not change in the future. There have besides been ways of dealing with artillery and aviation of the opponent.
In the case of unmanned aircraft, 3 planes have been found to be utilized at the moment:
- Recognition – at different levels and for different formations,
- Air combat – in terms of the demolition of targets on land, but most likely shortly those in the air
- Artillery combat – unmanned, as circular ammunition, utilized alongside conventional and rocket ammunition.
When unmanned aircraft are utilized in reconnaissance tasks, these devices simply increase the efficiency of a given formation: infantry, artillery, aviation or cavalry (tank/air).
In the case of air combat, unmanned vehicles are cheaper carriers of weapons systems, which are besides smaller, and thus have less capabilities than aircraft.
In the case of artillery combat, circulating ammunition has the advantage that it may be launched/used before the mark is targeted. In another words, in the first phase of usage the drone is utilized to admit the target, and only later it turns into a rocket (a double role). However, it should be remembered that unmanned aircraft fly slower than barrel or rocket artillery shells. So they can be easy shot down or neutralized in any another way. They can lift a smaller explosive, which makes them little effective. In the future there may be swarms of drones, but for the present day, it is much easier to halt an opponent with a firestorm made by 3 units of artillery than send into the air 100 kamikaze drones, each of which must be operated by 1 operator.
Nevertheless, the massive usage of tiny unmanned workers creates large opportunities for recognition, as well as certain – although powerfully exaggerated present – the ability to destruct targets. surely the function of unmanned people on the battlefield will grow.
That's why we've been working on systems for respective years. multilayer anti-drone defence. Systems based on technologies have proven effective: microwave, laser, radio-electronic combat, guided anti-aircraft missiles, and yet besides anti-aircraft barrel artillery of various calibers (which is supported by computers).
Implementation to the future army of multi-layered drone defence (used both by an infantry soldier and placed on lighter or heavier fighting cars or placed on infrastructure facilities) will most likely produce the same effect,how to make and implement modern anti-aircraft systems to limit the usage of aviation.
In another words, it should be assumed that due to the action of area equipment (e.g. by utilizing radio-electronic combat systems)) or even point (missile systems, barrel artillery, microwaves and lasers) It will be possible to neutralise hostile actions carried out with unmanned workers including autonomous combat systems for a shorter or longer period (e.g. for the time taken at the location of the contact operation).
This leads to the conclusion that Future armies must be able to carry out effective: reconnaissance, artillery combat, air combat – without utilizing unmanned systems. If, by focusing on modern technologies, an army develops in specified a way that it loses its "traditional" competence in this area, then it can be condemned to defeat in the fight against an opponent who has the ability, even temporarily, to neutralise unmanned workers (more or little autonomous).
The usage of fresh forms of reconnaissance, air combat or artillery with the aid of unmanned aircraft – as with the improvement of radars and another reconnaissance systems, as well as artillery or aviation – will not affect the usefulness of infantry, cavalry, artillery or aviation on the battlefield. Only ways of fighting these formations and their tools can change (i.e. an unmanned tank, although it is hard to imagine that individual chooses to build an costly and dense car that could be neutralized without firing by radio-electronic or another systems).
Super Infantry and Return of Weapons of Mass Destruction

There is no uncertainty that with the improvement of various formations and the emergence of fresh battlefield domains, the infantry – possibly the oldest formation – besides developed. As she erstwhile had to deal with cavalry (e.g. with spades and utilizing obstacles) so present there are tools for infantry to fight aviation, cavalry, artillery (e.g. circular ammunition) and yet another infantry.
In any situations the function of infantry even increased. Without doubt, if it is utilized in a mass way, it can be a major problem for the enemy. A problem that has already been solved in the past. In the form of weapons of mass destruction. The claim that in future wars no 1 will usage specified a war can be verified as brutally as the claim that in modern war no 1 will carry out war crimes and attack or abuse the civilian population. Therefore, an army preparing for a future war should take into account the hazard of utilizing all kinds of weapons against it.
Current improvement direction: minimisation of weapon systems, resulting in increased universality and combat efficiency of infantry
Future battlefield (expected abilities): return to area weapons/mass demolition effective against infantry (chemical, biological, radiological, thermobaric, napalm etc.),
Necessary possible for the future army: systems protecting the infantry, i.e. dense combat vehicles, inexpensive and light modular battlefield shelters, fresh technologies utilized in the manufacture of military protective clothing
A fresh kind of field-fired weapon?
The usage of nuclear, biological, or even chemical weapons has certain long-term effects. The irradiation or contamination may impede or even prevent the usage of a given site or infrastructure by a organization which itself decides to usage the above-mentioned combat measures. Therefore, it should be assumed that the usage of specified a means of damaging the parties to the conflict will be decided on the ultimate.
For this reason, it is highly likely that the future precedence for the improvement of military technologies will be specified a kind of weapon that will be highly effective in the area-wide extermination of the surviving force in the selected area, and which will not have any adverse effects on the side utilizing the weapon described. specified a feature now possesses thermobaric weapons, whose improvement may be crucial. Not only in the context of possible aggression, but besides in defensive application, especially in its own territory.
Cassette ammunition, mentioned napalm, or phosphorus ammunition can besides return to grace. It should be remembered that erstwhile the global order falls (and with it institutions), authoritarian governments may not want to follow any rules.
Precious dense equipment

Expensive and time-consuming dense equipment in production will most likely weigh gold on the future battlefield. Combat vehicles – in consequence to the improvement of lighter anti-tank systems (i.e. circulating ammunition, anti-tank missiles, mines) and precision artillery – can become heavier due to the request for better protection (passive and active systems). The weight of wagons will require wider usage of track traction. The increase in production and maintenance costs will make armored wagons and tanks will become even more versatile. And thus more useful. However, the problem may be mass production and restrictions in industry, where breaking supply chains could mean a deficiency of adequate components to make fresh vehicles in the course of war (refilling losses). So combat cars can become more valuable, their failure more painful, and the advantage on the battlefield can be determined by the "output" resources, and thus the wagons with which the organization will start conflict. As during the war in Ukraine, it may turn out that the fighting state, even if it maintains the production capacity of a given kind of vehicle, is only in the mediocre version (due to the deficiency of previously imported technologies).
Combat vehicles will be crucial not only in terms of offensive possible and maneuverability. With respect to the anticipation of returning to the usage of area/mass demolition measures on the battlefield, combat vehicles may be 1 of the forms of protection of infantry against the abovementioned measures. They will proceed to be an crucial part of the protection of soldiers, as well as the transport of adequate equipment for them. Unmanned aircraft, anti-aircraft and anti-tank missiles, radio-communication equipment, individual weapons and ammunition supplies. The ability to actively support infantry on the battlefield will be even more crucial due to the anticipation of utilizing better optics and various types of equipment to detect enemy positions, which a fast-paced squad of soldiers could not take with them.
Importantly, tank companies may include combat vehicles for unmanned docking stations. expanding designation for armored sections will, among another things, enable the recognition or avoidance of ambushes and anti-tank opposition points. possibly more extended usage will be made of caterpillar drones to identify the way of the planned journey in the context of mine hazards.
Current improvement direction: development of active and passive vehicle defence systems against different anti-tank systems,
Future battlefield (expected abilities): high saturation anti-tank, even heavier and more versatile combat cars,
Necessary possible for the future army: development of reconnaissance systems to support heavier combat vehicles, including in order to avoid ambushes and well-prepared opposition points, and, above all, to grow the dense weapons manufacture before the conflict
Blitzkrieg eternal alive
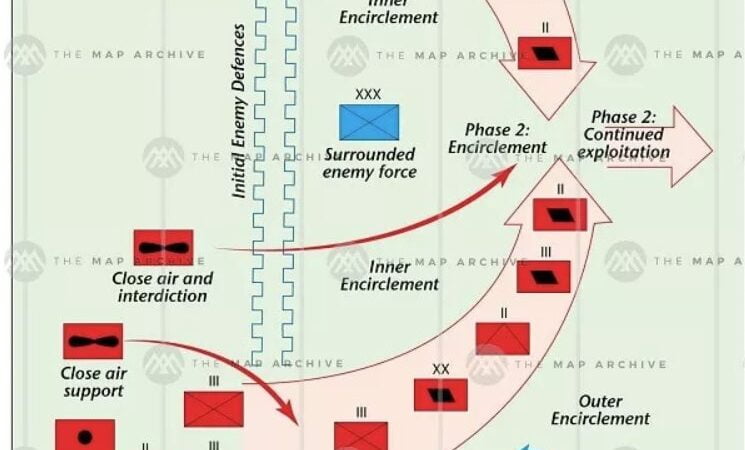
The mine fight can again become a key and indispensable form of action, so that overhead mines vehicles and specialised minefields can be utilized on a massive scale. The effectiveness of specified tools in the defence (in combination with artillery and good diagnosis) is confirmed by experiences from the Ukrainian front. specified a conclusion from this conflict may inactive be valid for a long time.
Current direction of development/experience: Mutilation vehicles and peculiar bomb wagons,
Future battlefield (expected abilities): more massive usage of minefields, which can be an effective tool for supporting defensive action even on a broad front, future aggressors will effort to prevent a static phase of conflict with minefields, so the first phase of war (decisive) will aim for fast settlements through the force of fire and maneuver,
Necessary possible for the future army: the ability of the full state apparatus to foretell a possible attack before it occurs, the possible to halt the enemy's first momentum, the ability to have both a defensive static war and utilizing maneuvering and counterattacking, the possible to carry out a preemptive attack,
Civilians for slaughter and protective infrastructure

History has repeatedly shown that the business of a given territory usually ends and that those occupied sooner or later, with political action or armed resistance, regain control of the inhabited region. On the another hand, sustainable effects can be achieved through drastic measures – vide Stalin's mass resettlement after 1945 or the cleansing and genocide utilized during WWII. specified conclusions were most likely besides reached by Putin in 2022 deciding to repress Ukrainians in occupied territories.
Future full-scale wars can become even more cruel. Due to the advanced cost of conflicting, aggressors will care for lasting prey. specified effects as can no longer be undone. The worst, i.e. conflicts driven by ideology and chauvinism, in which action against the civilian population will be 1 of the priorities, should be assumed.
Current direction of development/experience: The wars have always active cruelty to the civilian population, and the war in Ukraine proves that, unfortunately, small has changed in this matter,
Future battlefield (expected abilities): possible mass repression of the conquered civilian population,
Essential possible for the future army/state: the possible to remove the threat from the borders of its own country, as well as an extended civilian defence infrastructure in case the opponent uses weapons of mass demolition or terrorist fire at civilian centres, as well as appropriate measures and procedures to guarantee the fast and safe relocation of residents from the area at hazard at previously prepared temporary residences.
The territory can be recovered, the infrastructure rebuilt, but there is no anticipation of resurrecting war victims. Protecting its own civilian population should be a precedence for the fighting parties. This can be done by dismissing and neutralizing threats, temporary displacement of civilians or by ensuring adequate safety infrastructure (i.e. shelters).
Ambitious targets require large armies

I have described above the assumptions, as well as the directions of current improvement in the field of tools and their usage on the battlefield. Importantly, I tried to foretell what the mark effect of modern improvement would be like, and, most importantly, how in the future countries and their armies will effort to deal with circumstantial solutions that will be implemented.
In view of all the above, it can be concluded that future armies – whose aim will be to knock down the full country (or even a few) – they will should be huge. specified wording is prompted by the following factors:
- The experience of Russians in the war in Ukraine, where it turned out that 100-200 1000 soldiers were a force besides modest to accomplish the goal rapidly (the Kiev occupation, the taking over of power over Ukraine).
- The determination of defenders may in the future be the same as the Ukrainian 1 (although it may be observed that this kind of mass opposition can be effective), and so the future attacked states can be prepared to exposure even a million people to arms, which makes you think of the war in conflict with the First or Second planet War.
- The war in Ukraine is simply a certain minute of a breakthrough, after which 1 should anticipate an arms race, as well as an increase in army numbers.
- Future military technologies will let to repel the enemy in an even more precise but massive way – which will drastically change the calculation of possible war losses. This in turn will encourage possible aggressors to increase – not decrease – the army's size. On the Western Front of the First planet War, artillery massacred infantry formations. The consequence was not the withdrawal of the infantry, but the mass conscription and creation of millions of armies.
It should be stressed again that The scale of the conflict depends more on the aggressor. This full survey is based on the presumption that in the future there will be full-scale conflicts which will aim to bring down the full country. And if specified wars occur, the intent of this article was to effort to answer the question: what can the future war look like?
The conclusion that the immense armed forces issued by NATO, for example, will discourage possible aggressors is as right as it has a certain – although unknown – expiry date. The example of Russian aggression of 2022 is surely a informing for modern rulers. For it turned out that To defeat the state with no top possible at all, it takes much more strength and resources than many have assumed. Especially erstwhile the country receives outside help. This leads to the conclusion that probably in the next fewer years no 1 else will decide on aggression on specified a large scale until they become certain of having the right advantage. Nowadays there are fewer armies in the planet that would be able to make fast victories against a country with akin possible as Ukraine. Therefore, considering future full-scale wars is very risky at the moment. Although it should besides not be excluded that wars of the described kind will be triggered by states not prepared for this, which would take specified a step due to utmost circumstances.
One way or another, NATO may not last forever, and after the collapse of the current global order, there will be specified planet powers as will want to resolve political issues with armed action. Then the larger armies will defend, or victims of aggression, the more forces they will want to attack aggressors.
This would prove to be false if, in the close future, the planet re-entered the consolidation, globalisation and stabilisation of the single-polar planet order. This would consequence in a renewed trend towards demilitarisation of the planet within the meaning of limiting the size of the individual armed forces to the minimum necessary. This kind of presumption can be made and defended. On the another hand, the author does not share the optimism expressed in specified perception of the ongoing political processes.
At the same time, while respecting the rule that it is always essential to be prepared for the worst-case scenario, it was essential to specify the script to be taken into account by the state in order to prepare for hard times.
There is simply a heated discussion in Poland about whether the planned form of the Land Army (6 divisions + independent regiments and brigades) is not very ambitious. On the basis of the above conclusions, fear that in 2035 or 2045 the army of 300,000 soldiers will be besides modest.
If the global order as we know the runes, and the powerful or ideological ambitions take precedence over common sense, then regimes governing future aggressor states can make millions of armies. specified a script is easy to foretell especially in the context of Asian countries, where the acquisition of adequate human mass is no problem. This in turn makes you ask a very crucial question: what will be the safety of much little populated and much worse on the demographic level of Europe? Will European countries be able to get a adequate technological advantage that will enable them to offset the numbers of Asia and Africa? What about mass migration? What European countries have a plan to defend their borders, values, technological advantages and achievements in the context of future threats?
Future full-scale wars will begin in Asia
There is no uncertainty that with the possible we have in Europe and as we can imagine in 10 or 15 years, European countries will not be able to initiate full-scale armed conflicts. Some countries may hold their possible for limited military interventions, but most of them may even have a problem gathering defensive needs.
This leads to a consensus that subsequent – after the war in Ukraine – full-scale conflicts in the planet will begin to erupt first in Asia.Where the state's technological level, industrialisation, but besides the size of the population can make appropriate military potential.
On the 1 hand, this seems comforting from the position of Europeans or Poles. On the another hand, it leads to the apparent conclusion that If Asia enters the era of territorial wars and conquest, 1 of the priorities of future military powers will be the Persian Gulf. If any Asian power could gain control of mediate east oil exports, then Europe could – assuming oil remains a strategical natural material – become the vassal of the “east” or even the next victim of aggression from that side.
The current threat from Russia should be considered temporary and in fact short-lived. This situation in Asia represents the biggest challenge for planet peace in the average and long term. It is there that there are countries with adequate resources in Asia (human, industrial, technological) to build an offensive army. At the same time, local societies are inactive active in the pursuit of Prosperity. In addition to Japan, South Korea, Taiwan and Singapore, the remainder of Asia is inactive on track. What if the dreams of wealth neglect and the situation even gets worse? How will interior crises be addressed by more or little authoritarian Asian governments?
If the West does not keep its current dominance in planet order, winter will come not from the north, but from the east.
Krzysztof Wojchal
geopolitics, politics, economy, law, taxes – blog



![MON upraszcza procedury zakupu dronów i systemów antydronowych [WIDEO]](https://zbiam.pl/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/signal-2025-09-19-082424-002.jpeg)









