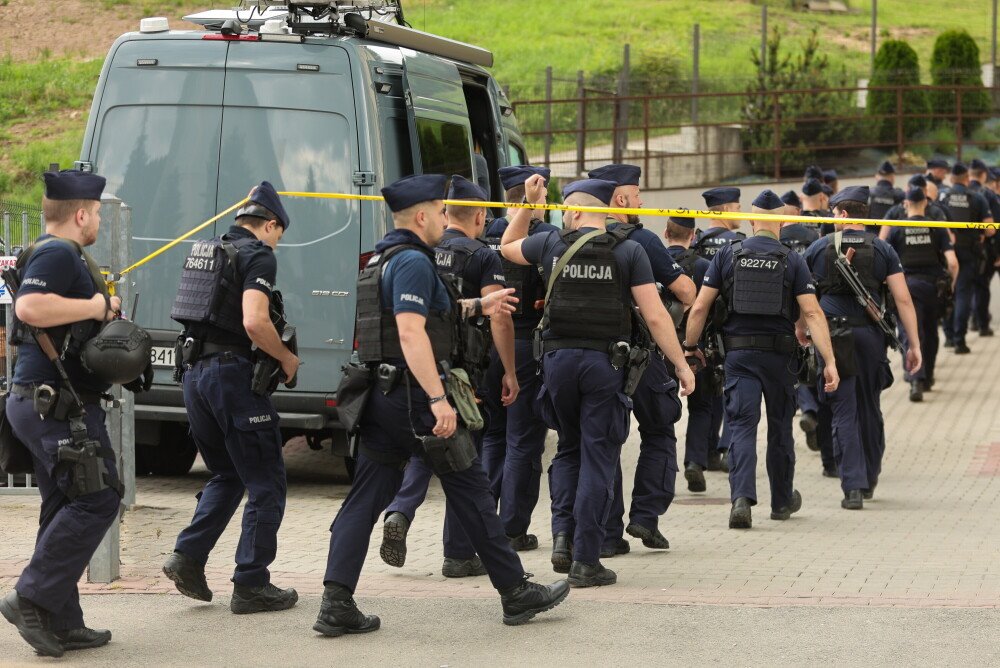
- Rigorous veterinary checks are carried out 24/7 at 10 passes, utilizing gates and disinfection mats
- On 21 March, imports of selected goods from Slovakia were banned due to outbreaks of foot-and-mouth illness in that country
- Poland remains a foot-and-mouth disease-free country, but intensifys prevention due to illness cases in neighbouring countries
- For more information, visit the Onetu homepage
Controls are carried out by the Central Inspectorate of Road Transport (GITT) together with officers of the National taxation Administration, Border defender and Police and with veterinarians in the two-shift system, besides on weekends.
The Ministry of Infrastructure stated that about 250-300 animal transport controls are carried out regular in the Opole state at the border crossing with the Czech Republic in Trzebina. So far, 4,000 have been carried out. On the another hand, in the Silesian province, at the crossings in Chalupki, Cieszyn and Gorzyczki (also the border with the Czech Republic) there were over 15,000 specified controls.
The Provincial Inspectorate of Road Transport (WITD) in Katowice conducted about 5.5 1000 of them. "In more than 20 cases, the decision to retreat the vehicle from Poland was issued," added the ministry. Controls are besides carried out in Podkarpackie province, with the support of inspectors from WITD in Krakow, and in the future the activities can be extended to WITD area in Wrocław.
Border checks
‘Poland is inactive a country where no foot-and-mouth illness virus has been found, and intensification of preventive measures is related to the hazard of transmission of the virus from neighbouring countries where the illness occurs," the ministry stressed. It informed that a crisis staff gathering on foot-and-mouth illness was held on Thursday, attended by representatives of the MI department, GITD, and subsequent meetings “will be held regular until further notice”.
On Wednesday in the Sejm, Minister of Agriculture and agrarian improvement Czesław Siekierski said Whereas strict veterinary checks have been introduced at the confederate border due to the hazard of foot-and-mouth disease. He informed that at 10 border crossing points veterinary services were moving round-the-clock shifts, wickets and disinfection mats were set up. He pointed to Podkarpackie, Opolskie, Śląskie and Małopolskie voivodships.
Before that, Siekierski estimated that the threat of foot-and-mouth illness was serious due to the fact that the virus moved easy and in various ways. On 21 March, the head of the Ministry of Agriculture decided to close the territory of Poland to imports of selected goods from Slovakia due to outbreaks of foot-and-mouth illness in that country. The Regulation is to apply until the European Commission adopts the appropriate solutions.
Foot-and-mouth disease
In early January this year, German veterinary services reported the uncovering of the first case of foot-and-mouth illness in 37 years. The farm where the illness occurred was about 70 km from the Polish border. On February 19, the German services reported that 7,000 samples were tested for foot-and-mouth illness and that further cases of illness were not detected. the protection and surveillance zones have already been removed in Germany, and only the buffer region has been removed, as decided by the EC until 11 April.
At the end of March, the Polish Veterinary Inspection reported that a second outbreak of foot-and-mouth illness has been confirmed in Hungary close the interface between the Austrian, Czech and Slovak borders. The day before the outbreak of foot-and-mouth illness was reported by Slovakia. Due to foot-and-mouth disease, the Slovak government has introduced an emergency state throughout the country.
foot-and-mouth illness is highly contagious and dangerous to animals. In the event of an outbreak, all animals on holdings must be slaughtered. The illness besides affects chaotic animals. The last time foot-and-mouth illness appeared in Czechoslovakia in 1975, and in Poland, which is considered a free country from foot-and-mouth disease, in 1971.