- Forecasts are bad, and solutions are not visible. utmost reviews indicate that Europe will turn into a museum of monuments visited by tourists from Asia and North America
- There are no shortages of talented scientists or ambitious entrepreneurs in Europe. However, innovation here is blocked at the commercialisation stage. Turns out it's a strategy problem.
- European companies specialise in conventional technologies whose possible is limited and so spend little on investigation and innovation
- Last year sales of Volkswagen vehicles decreased by 1.4%, to 4.8 million, and operating profit of the company decreased by almost 37%.
- More crucial information can be found on the Onet homepage
In 1992, the European Union's contribution to global GDP was 29 percent. The German Volkswagen, Porsche and Audi cars were considered the best in the world. Siemens produced individual computers under the Siemens Nixdorf brand. In the UK, Alan Sugar headed the computer-producing company Amstrad. The Minitel video-text strategy introduced in France in 1982 was the most successful network service existing before the net was spread.
The Treaty on European Union, signed in Maastricht on 7 February 1992, created it as we know it today. The russian Union fell apart, and the resulting state breakdown plunged into crises. The United States' share of global GDP was 25.7%, and China was only 2% of Japan, which developed rapidly in the 1970s and 1980s, besides fell into crisis. European leaders were in a euphoria – everything seemed to be heading in the right direction. Today we know that 1992 was the beginning of the end of the dominance of the Old Continent.
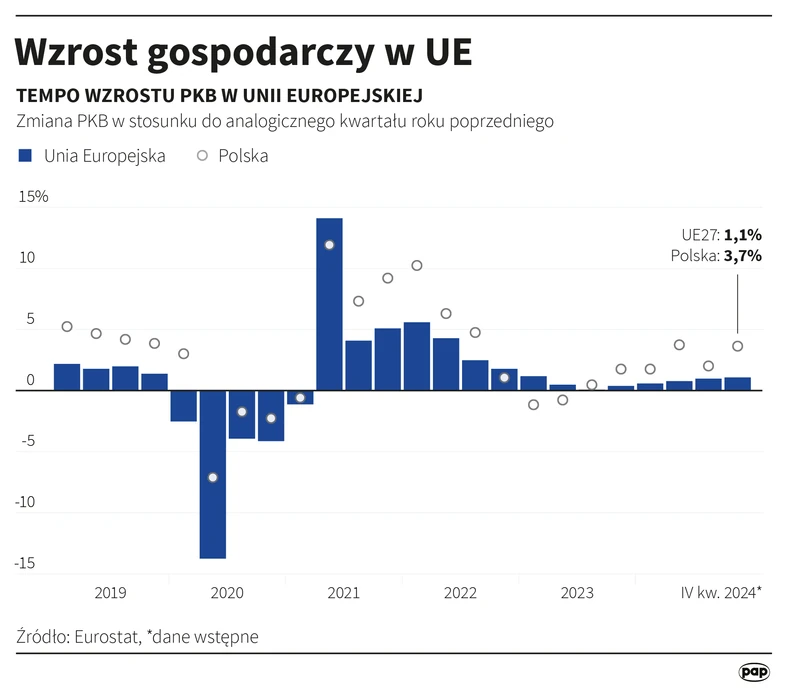
In 2024, Europe's share of global GDP was 17.5% and it is known to be falling. In the 21st century, the European economy lost its innovation and ceased to be competitive. German automobile companies are moving production to China and the United States. large chemical companies like BASF, too. Forecasts are bad, and solutions are not visible. utmost reviews indicate that Europe will turn into a museum of monuments visited by tourists from Asia and North America. What caused specified a deep fall?
Freedom, equality, brotherhood, and then what?
Why was the European Union created? At the end of the 20th century, German, French, British and Italian politicians believed that the main task of a united Europe was to supply societies with democracy, peace, freedom, justice and prosperity. The economy and its growth in terms of it were to be only tools to accomplish these noble objectives. Her condition was no concern – she was more powerful than the American and Japanese. And so innovative.
Management boards and supervisory boards of major European banks and corporations were held by managers equal to the age of members of the Political Office of the PCD. They were incapable to see the challenges that arose in the late 1980s and 1990s.
Western societies, freed from the threat of the russian Union, wanted to live a better life. Expenditure on wellness care and pension provision increased significantly.
In the '90s. Germany has borne immense costs of unification, and it was not in their head to supply for the innovation of companies. The same was felt in another countries. As a result, in the last 50 years, there has been no company in the European Union with marketplace capitalisation exceeding EUR 100 billion. Six were created in the United States – their capitalisation exceeded EUR 1 trillion.
There are no shortages of talented scientists or ambitious entrepreneurs in Europe. However, innovation here is blocked at the commercialisation stage. Turns out it's a systemic problem. European companies specialise in conventional technologies whose possible is limited and so spend little on investigation and innovation. In the last 20 years, automotive companies have invested most in investigation and development. This was the case in the United States at the turn of the 20th and 21st centuries. Today, technology companies are investing the most in the US.
European companies were incapable to make “own” Google, Facebook, Instagram, although the Chinese and Russians did. The French Minitel system, which overtakes the net by a decade, was not developed and is now history. European banks have been hit massively by the 2008 crisis and although they have overcame the problems over time, they proceed to prosecute a very conservative policy.
As a result, the cost of moving social policies increases with each year. In addition, Western European countries face Inflow of successive waves of immigrants, mainly from Africa, muslim countries, and more late from Ukraine, who are an expanding burden on budgets. There are besides pressures to increase spending on wellness care and pensions. This is due to the fact that entrepreneurs anticipate that the State will supply grants in case of trouble. For now, money is in the name of preserving European values and lifestyles. For this, economical growth is weak and the distance to the United States and China is growing. And no 1 knows how to halt the disaster.
 Mateusz Krymski / PAP
Mateusz Krymski / PAPAre you certain it's über alles?
The German economy was and is the most powerful in the European Union. The biggest German employer remains the automotive industry. Last year Volkswagen produced about 2 million cars little than in 2019. At the same time, he maintained a akin level of employment. It turned out that any of his plants utilized their production capacity in 20-30 percent.
Last year, it was reported that the company's management was considering closing at least 3 factories in Germany and releasing thousands of workers. This would be an unprecedented step in Volkswagen's almost 90-year history.
The increasing sales of electrical cars produced by Chinese companies in Germany were a sad circumstance. They were cheaper than German vehicles. And better equipped. Time will tell if they will be equally durable.
Last year sales of Volkswagen vehicles decreased by 1.4%, to 4.8 million, and operating profit of the company decreased by almost 37%.
 Filip vocalist / PAP
Filip vocalist / PAPVolkswagen automotive company mill in Wolfsburg
The problems were besides affected by BASF. Its sales in 2023 fell by over 21%, to EUR 68.9 billion from EUR 87.3 billion in 2022. As a consequence of the war in Ukraine, the subsidiary of the corporation, Wintershall Dea, had to retreat from Russia, resulting in write-offs of about €7.3 billion. present BASF is besides facing challenges of global economical slowdown, advanced energy costs, geopolitical tensions and the request for restructuring. And it announces a simplification in employment in German factories. But he's not giving up his investment in China. There was besides information about plans to launch production in the United States. For Germans, that's bad news.
Throughout 2023 the national Statistical Office recorded 17 1000 814 companies' bankruptcy. The year 2024 proved even worse. Between January and August, the courts reported 14 1000 403 cases of bankruptcy of German companies, which meant an increase of about 23 percent compared to the same period in the erstwhile year. According to credit agency Creditreform forecasts, the full number of bankruptcies last year could scope 22.4 1000 entities. Forecasts for 2025 are even worse. There may even be 30,000 companies falling.
In the media, there is frequently an increase in energy costs, which is two-three times higher in Germany than in the United States and China, as a origin of economical problems. Therefore politicians of the right-wing alternate organization for Germany (AfD)demand the restoration of gas supply from Russia, the abolition of sanctions and the return to the former, mutually beneficial, trade. The economies of another Western countries have almost identical problems. And there's no indication that this will change.
Interestingly, the European Union inactive has a surplus in trade with the United States. In 2021 it was almost 166 billion euro and 158 billion in 2023. president Donald Trump late referred to this deficit as a "wild beast" and stated that "the Union has crossed borders", so "for sure" duties will be imposed on European goods. shortly we will see whether it was a militant introduction to negotiations or the beginning of the trade war, which will deepen the economical problems of the Old Continent states.
What limits Europe?
The list of causes of problems for EU countries is long. surely 1 of the most crucial are the advanced energy costs associated with the war in Ukraine and the cut off of Europe from inexpensive Russian gas. The increasing labour, materials and general business costs are besides an crucial cause. The brake is besides a restrictive monetary policy and advanced interest rates which increase credit costs.
This includes demographic problems and shortages of workers, especially those with advanced qualifications, which negatively affects business development.
The fall in the real income of the population translates into rising consumer savings and lower spending. Markets are besides destabilised by geopolitical tensions and armed conflicts, which contribute to breaking supply chains.
The EU's sanctions on goods and services sold and purchased in Russia are crucial circumstances. Therefore, no 1 should be amazed by the stagnation of investment in the largest EU economies, with German leading, which translates into a decline in competitiveness towards the United States, China or India. The Green Deal policy, which the Union intends to define, proved to be costly, due to the fact that it has not officially withdrawn from it.
When we talk about implementing ambitious programmes, European experiences are as bad as possible. Just mention the Lisbon strategy adopted by the European Council in March 2000. Its aim was to make EU countries the most dynamic and competitive economical region in the world, developing faster than the United States, within 10 years. The Lisbon strategy was based on the presumption that our economies would become more innovative Thanks to extended research, the results of which will be applied in modern industries. The objectives were set: R & D spending in EU countries would increase to 3% of GDP in 2010, bureaucratic rules would be reduced to hinder business growth, and employment would increase.
 Weekly Review
Weekly ReviewAs early as 2005 it was clear that the implementation of this strategy was going poorly, and the improvement gap between the United States and Europe is growing. The main reasons for this were the weak coordination of actions, the conflicting objectives set out in the strategy, its excessive scope and the deficiency of determination by associate States.
According to the data of the European Union of Chambers of manufacture and Trade published after 2010, the European Union's deficit in GDP, in terms of competitiveness and in terms of backing discipline to the United States was 20-30 years.
The opposition of EU countries to reducing extended social advantages, which provided support to governments but generated immense costs and reduced competitiveness, was pointed out. It has been said that Europeans work little than Americans or do not work at all, surviving with social assistance. As a result, Europe's main weakness was not the problems with the knowledge-based economy, but overdeveloped social systems and the peculiar protection of workers. On the 1 hand, this has led citizens of EU countries not to work, on the another hand, to discourage employers from creating fresh positions. And the wheel closed.
The situation has deteriorated since 2010. The 2008 crisis, which began with the collapse of the American bank Lehman Brothers, hit the European economy with all its might. In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic reached Europe, and in February 2022 Russian troops invaded Ukraine. Today, in the face of many threats, the future seems more uncertain than a decade ago. And Europe turns into a migrant-occupied open-air museum.












